Wastewater Treatment without additional Chemicals
EAOP® (Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Process)
There are many types of pollution in wastewater: toxic substances, with poor biodegradability and persistent substances such as drug residues. These accumulate particularly in industrial production processes or the commercial use of hazardous substances. We have developed a process for oxidative wastewater treatment that is suitable for the removal of a wide variety of pollutants.
Our CONDIACELL® cells, which are equipped with diamond electrodes, are suitable both for total oxidation, i.e. use at high pollutant concentrations and low volumes, and for electrochemical polishing applications at low pollutant concentrations and high volumes.
Our EAOP® can be easily combined with other wastewater treatment processes.
The Advantages of Wastewater Treatment with EAOP®
Low space requirement
Modular design
On / off functionality
Easy maintenance
No waste
No addition of chemicals
This is how Wastewater Treatment works
Cold Incineration by Hydroxyl Radicals
Only hydroxyl radicals are formed on DIACHEM® electrodes by water electrolysis. The EAOP® with DIACHEM® diamond electrodes uses the hydroxyl radicals produced for industrial waste water treatment.
Hydroxyl radicals cause a "cold incineration" of organic substances. This works with all organic compounds dissolved in water. Responsible for this extensive range of action is the high oxidation potential of the hydroxyl radicals - with their highest current yields they trigger this conversion of substances.
Proof in Practice
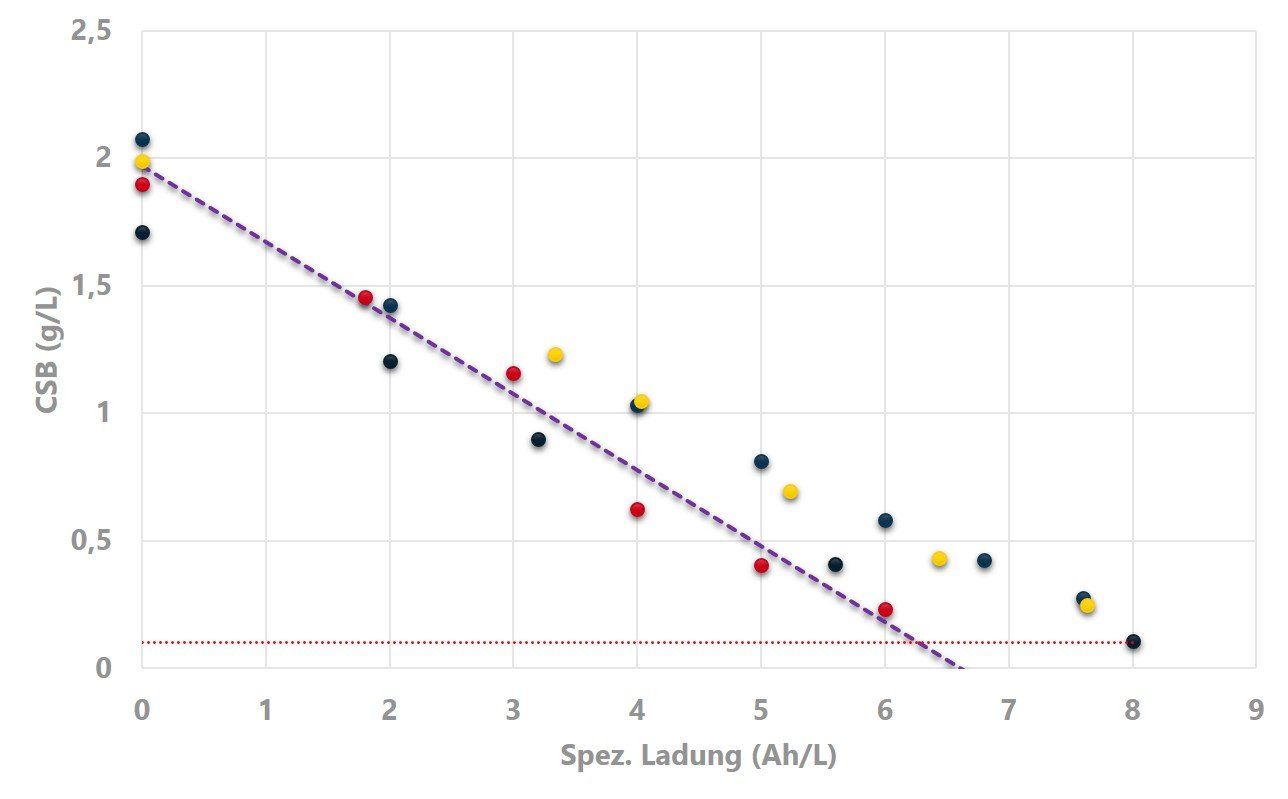
Wastewater Treatment in the Paper Industry
The results of waste water treatment in the paper industry show that the CONDIACELL® cell model CC5000 has achieved the degradation of organic pollutants (here indicated in COD) to the target value (red line) with an efficiency of up to 100% (dashed line) of the used electricity.
The results of wastewater treatment in the paper industry also show that the CONDIACELL® cell model CC5000 reduces the degradation of the organic pollutant EDTA > 80%. The reduction of this individual substance is faster than the reduction of the total organic load (here COD).
Here it can be seen that - by using EAOP® - individual critical water components can be reduced in accordance with the objectives of wastewater treatment in order to make them biodegradable without having to reduce the total organic content accordingly.
Wastewater Treatment in the Automotive Industry
The results of wastewater treatment in the automotive industry show that the CONDIACELL® cell model CC5000 can reduce the total amount of organic pollutants without any loss of efficiency of the electrolysis flow.
Thus, by selecting the appropriate operating parameters of cell and wastewater flow, maximum efficiency of wastewater treatment processes can be achieved in the corresponding industry.
The results of wastewater treatment in the automotive industry show that the CONDIACELL® cell model CC5000 can reduce the degradation of poorly biodegradable organic pollutants - in this case a surfactant - in accordance with the limit values to be observed (red line) and even beyond.
This is also possible efficiently if the pollutant is present in concentrations in the mg range as part of an organic content of several g/L